All You Need to Know About Abdominal Hysterectomy and Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy
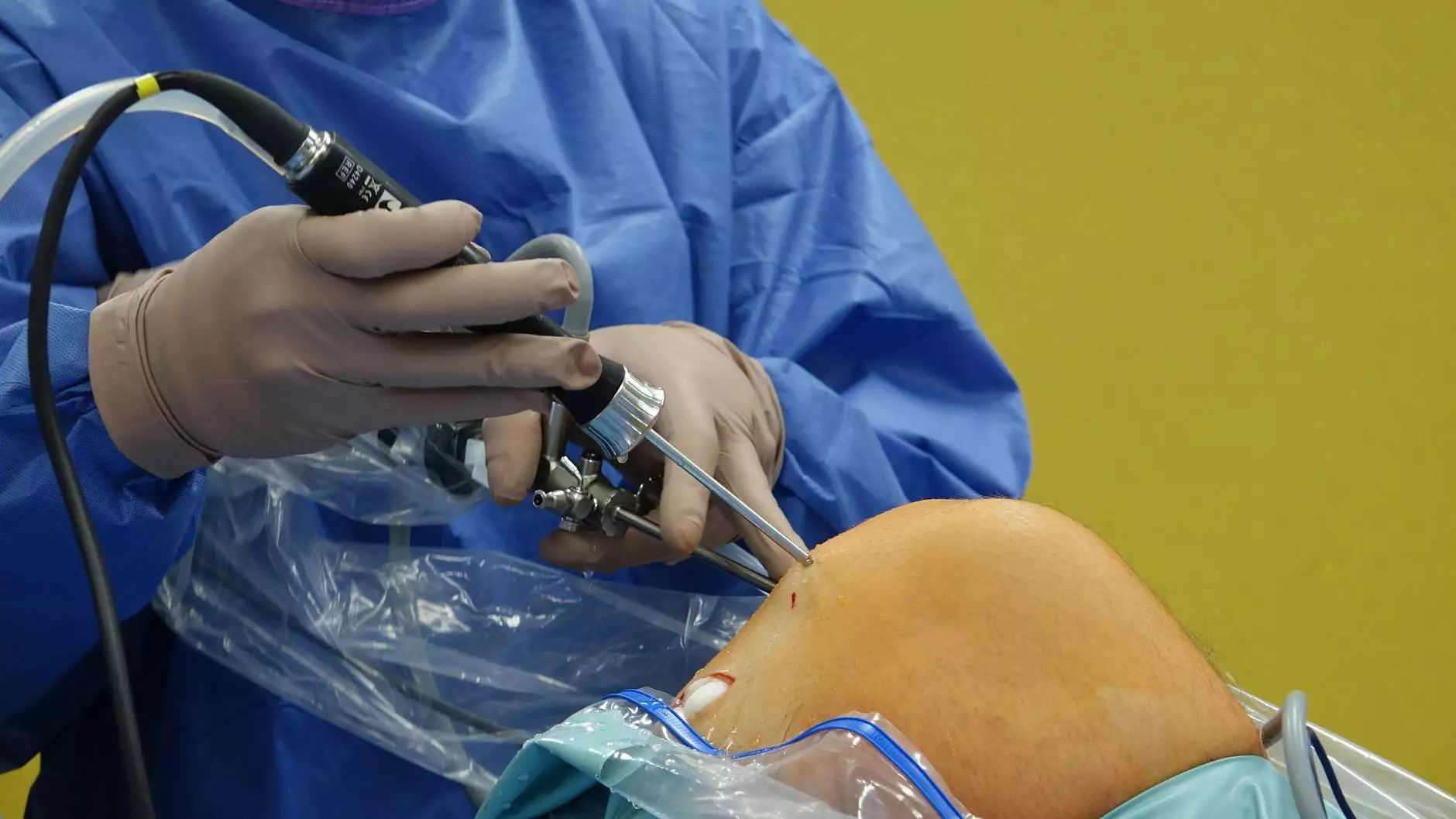
Abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy are surgical procedures that play a crucial role in women’s health. They are often performed to treat various gynecological issues, including fibroids, endometriosis, and cancer. Understanding these practices, their indications, benefits, and recovery processes can empower patients and their families to make informed healthcare decisions.
What is Abdominal Hysterectomy?
An abdominal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus through an incision in the abdominal wall. This surgery may also include the removal of the cervix, and sometimes, adjacent structures such as fallopian tubes and ovaries depending on individual patient conditions. This procedure is often recommended for:
- Uterine fibroids
- Severe endometriosis
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Uterine prolapse
- Cancer of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries
What is Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy?
Bilateral salpingo oophorectomy refers to the surgical removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes. This procedure is frequently performed simultaneously with an abdominal hysterectomy in cases where there is a risk of ovarian cancer or when significant ovarian issues arise. Indications for this surgery may include:
- Ovarian cancer or potential risk
- Endometriosis affecting the ovaries
- Severe ovarian torsion
- Ovarian cysts that cause severe symptoms
Indications for Combined Procedures
In cases where both an abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy are indicated, the combined procedure offers several advantages:
- Comprehensive treatment: Addressing multiple underlying conditions in one surgery.
- Reduced time under anesthesia: Minimizes the risks associated with multiple surgeries.
- Single recovery period: Simplifies the recovery process for patients.
The Surgical Procedure: What to Expect
Preoperative Preparations
Before undergoing an abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy, patients will undergo a thorough evaluation, including:
- Physical examinations
- Blood tests
- Imaging studies (e.g., ultrasounds, CT scans)
- Consultations with specialists
The Surgical Process
The surgery typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours and may be performed under general anesthesia. The surgical steps generally include:
- Creation of an abdominal incision (either vertical or horizontal, based on the surgeon’s guidance).
- Careful dissection to access the uterus and associated structures.
- Removal of the uterus, cervix, and any necessary associated organs (i.e., ovaries and fallopian tubes).
- Closure of the incision with stitches or staples.
Benefits of Abdominal Hysterectomy and Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy
Patients opting for these surgical procedures can experience numerous positive outcomes, including:
- Pain relief: Significant reduction or elimination of chronic pelvic pain.
- Management of heavy bleeding: Resolving severe dysmenorrhea or menorrhagia.
- Reduced cancer risk: Preventative measure against ovarian and uterine cancers.
- Quality of life improvements: Enhanced physical and psychological well-being post-surgery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After surgery, patients can expect a recovery period that varies depending on individual circumstances. General postoperative care includes:
- Monitoring vital signs in a recovery room.
- Managing pain with prescribed medications.
- Gradual introduction of food and fluids.
- Incentives for mobility to prevent blood clots.
Recovery Timeline
The typical recovery timeline involves:
- Hospital stay: Usually 1 to 2 days for observation.
- Return to normal activities: Light activities after 2-6 weeks, full recovery may take 6-8 weeks.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any major surgery, risks are involved. Possible complications of abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Infections
- Damage to surrounding organs
- Anesthesia-related complications
- Blood clots
Long-term Considerations
Post-surgery, patients may have long-term considerations, particularly regarding hormone therapy if ovaries are removed. Key aspects include:
- Menopause symptoms: Awareness and management of menopausal symptoms, if applicable.
- Bone health: Importance of calcium and vitamin D for bone density.
- Routine check-ups: Keeping up with gynecological health assessments.
Conclusion: Empowering Informed Choices
In summary, understanding the procedures of abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy empowers women to make informed decisions regarding their health. By discussing options and potential outcomes with healthcare providers, patients can pursue the best treatment strategies tailored to their specific needs.
For more information and support regarding gynecological health, please visit drseckin.com, where expert care and insightful resources are readily available.